Nhà cung cấp: Công Ty TNHH TM An Vĩnh Phát
Địa chỉ: 79/6c Quốc lộ 13, Phường 26, BT
Quốc gia: Vietnam
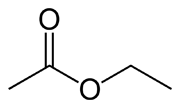
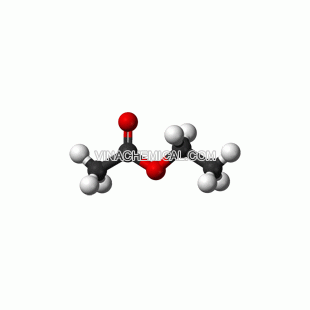
ETHYL ACETATE
Giá:
Ethyl acetate (systematically, ethyl ethanoate, commonly abbreviated EtOAc or EA) is the organic compound with the formula CH3COOCH2CH3. This colorless liquid has a characteristic sweet smell (similar to pear drops) like certain glues or nail polish removers, in which it is used. Ethyl acetate is the ester of ethanol and acetic acid; it is manufactured on a large scale for use as a solvent
Ethyl acetate is synthesized industrially mainly via the classic Fischer esterification reaction of ethanol and acetic acid. This mixture converts to the ester in about 65% yield at room temperature:
CH3CH2OH + CH3COOH ⇌ CH3COOCH2CH3 + H2O
The reaction can be accelerated by acid catalysis and the equilibrium can be shifted to the right by removal of water. It is also prepared industrially using the Tishchenko reaction, by combining two equivalents of acetaldehyde in the presence of an alkoxide catalyst:
2 CH3CHO → CH3COOCH2CH3
Ethyl acetate is synthesized industrially mainly via the classic Fischer esterification reaction of ethanol and acetic acid. This mixture converts to the ester in about 65% yield at room temperature:
CH3CH2OH + CH3COOH ⇌ CH3COOCH2CH3 + H2O
The reaction can be accelerated by acid catalysis and the equilibrium can be shifted to the right by removal of water. It is also prepared industrially using the Tishchenko reaction, by combining two equivalents of acetaldehyde in the presence of an alkoxide catalyst:
2 CH3CHO → CH3COOCH2CH3
CH3-CO-CH3

LIÊN HỆ ĐẶT HÀNG
Vui lòng nhập đầy đủ thông tin của bạn để gửi email
DANH MỤC















 Hóa chất tinh khiết
Hóa chất tinh khiết